It is charging into 2026 with a complete shift in the blockchain world – out of mere debates about digital money and into a radical reinvention of infrastructure. Zero-knowledge (ZK) technologies and blockchain architecture – modular.s are at the centre of that change. They are not mere buzzwords and are redefining the way blockchains scale, how they secure data and address some of the most challenging problems in the industry. (chainstack)
During the past several days, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin announced the biggest breakthrough: ZK-Ethereum Virtual Machines (ZK-EVMs) are now at alpha-level performance, and data availability sampling (PeerDAS) is already operational on mainnet. This alliance is driving Ethereum even further in eliminating the blockchain trilemma – that is, providing security, decentralisation and scalability simultaneously.
The blockchain story of today is no longer a story of high prices and unfulfilled promises. It is about creating actual solutions that render blockchain handy, effective and prepared to be utilised in the mainstream, finance and game applications, as well as identity and enterprise. This is what this might imply in 2026 and beyond.

ZK tech and modular blockchains are making Ethereum faster, secure, and scalable for 2026. (Image Source: Blockchain Reporter)
The Making of a Game-Changer at ZK Tech
The initial claim made by blockchain was audacious: decentralised and secure networks that eliminate the middlemen. However, with the increase in blockchains, scalability and privacy began to act as trip hazards.
Introduce zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) – cryptographic functions that can be used to convince one party that the statement is true without them knowing what the data was. In plain English: you can demonstrate that something is true without telling how it was done.
It is no longer academic cryptography. ZK tech has grown to the stage where it supports scalable rollups, privacy protocols and validation layers which can support thousands of transactions per second at costs much less than traditional networks.
ZK-EVM Ethereum Scaling the Future
The shift of Ethereum explains the direction that the ecosystem is moving. ZK-EVMs are special-purpose virtual machines that, under the Ethereum compatibility, execute smart contracts, but with zero-knowledge proofs to verify the execution off-chain and then permanently settle on the main chain.
This means:
- Batched transactions and the off-chain proven transactions can be verified using compact proofs on Ethereum.
- Gas expenses are reduced considerably.
- Security is tied to the mainnet of Ethereum.
- EVM compatibility is given to developers without having to rewrite contracts.
Buterin recently noted that a partial implementation of ZK-EVMs will likely happen in 2021, with their usage becoming the case in ZK-EVMs by 2027-2030. It is a paradigm change in the way one of the most significant blockchains in the world will work.
The New Blueprint of Modular Blockchains
If ZK tech is re-inventing the process of verifying transactions, modular blockchains are also re-inventing the concept of blockchains themselves.
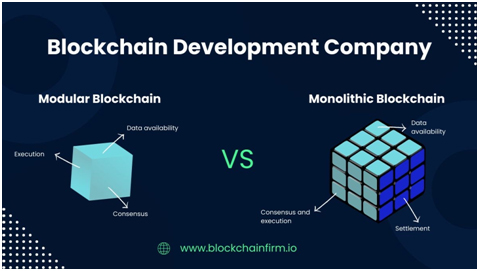
Modular systems separate consensus, execution and data availability functions by differentiating between layers of specialisation instead of a single, monolithic chain. It is a game-changer in terms of performance and flexibility. (gate)
The modular architecture can be decomposed in the following way:
- Execution Layer: Deals with smart contracts and transactions.
- Consensus Layer: Makes sure that there is a consensus regarding the order of transactions.
- Data Availability Layer: Ensures that data is available to anyone, but does not overload base chains.
The decoupling of these roles enables networks to scale much more effectively and enables developers to tailor chains to particular use cases – gaming to high-frequency DeFi.
This modular charge is being spearheaded by projects such as Celestia, StarkNet and zkSync Hyperchains. They allow execution layers to be connected to different data availability layers, which lessens the congestion and minimises the fees without compromising security.
Modular blockchains split layers to scale efficiently and cut fees without sacrificing security. (Image Source: UPay Blog)
Why This Matters in 2026
Scalability is the Only Way to Implement Mass Adoption
The adoption of blockchain had been stagnant due to the inability of the infrastructure to meet demand for a number of years. Users and enterprises were scared away by high gas charges, low throughput and low privacy.
The modular design and ZK tech change all that. They make blockchains:
- Faster
- Cheaper
- More secure
- More adaptable
It’s not theoretical anymore. These technologies are not speculative at all, as they are being tested and rolled out on large networks – and that is the difference in 2026.
Innovation Unleashed by the Developer
Developers do not develop on an all-purpose stack anymore. They can customise blockchains to certain needs:
- Data-heavy applications
- Privacy-centric services
- Gaming economies that have high throughput.
- Financial systems that require high levels of compliance.
ZK technology and modular designs offer the flexibility to create purpose-built chains, and entirely new classes of Web3 applications become possible.
Business-Friendly and Compliance-Friendly Blockchain
A regulatory risk and exposure to data are common, which pushes enterprises away in favour of Web3. ZK proofs provide an avenue to demonstrate adherence or authenticate action without data disclosure, which is a massive salvo to custodians, banks and governments.
Real-World Relevance Today
Recent improvements of Ethereum emphasise the move between the abstract and practical performance augmentation:
- PeerDAS is a system to sample data availability that is already in operation on staging areas of the mainnet of Ethereum. It allows the light clients to check block data at low cost.
- ZK-EVM implementations have been able to get to the production alpha performance, which is a stepping stone that can mean that it is time to expand the integration.
- The roadmap of the network tries to use these technologies to unlock more gas limits and throughput without leaving decentralisation.
Now that ZKEVMs are at alpha stage (production-quality performance, remaining work is safety) and PeerDAS is live on mainnet, it’s time to talk more about what this combination means for Ethereum.
These are not minor improvements; they are shifting Ethereum into being a…
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) January 3, 2026
Powering the ZK and Modular Wave Leading Projects
There is a grouping of solutions and platforms of proof-of-work products and products throughout the ecosystem that are becoming leaders in the ZK and modular space. These are not fringe technologies, but platforms of technology actually in use and being developed.
Linea: ZK Rollups at Scale
With ConsenSys as its backer (the team behind MetaMask), Linea has soared in popularity due to the ease of use with wallets and developer tooling. Its ZK-EVM rollup provides rapid and low-cost roll-up on top of Ethereum with high compatibility with Ethereum applications. The fact that Linea is focused on security and compliance is a strong point towards institutional and consumer adoption.
Zircuit – Hybrid ZK Architecture
Zircuit is a more recent player which implements zero-knowledge proofs together with hybrid fraud detection solutions. Its design combines functionality and increased safety – a key point that applications requiring speed and reliability, like DeFi and high-frequency trading, need.
Manta Pacific – ZK Modular Ecosystem
Manta Pacific was originally an L1, then became modular, powered by ZK, with easy developer onboarding and modular data availability. It is easier to create consumer-facing blockchain applications, with privacy and high throughput, using its approach.
Aleo Privacy-First ZK Programmable Chain
Aleo goes even further than others by maximising privacy by full privacy, using zero-knowledge proofs to power smart contracts. This will appeal to applications that need secrecy, like identity systems, confidential data market and safe voting.
Eclipse Solana VM and ZK Modular Rollup Eclipse
Eclipse integrates the high-speed Virtual Machine (VM) of Solana and ZK provers to produce one of the speediest modular rollup settings. This combination demonstrates the ability of modular architecture to combine the finest features of various ecosystems.
Celestia and zkSync Hyperchains – Modular Connection
Celestia, which are modular blockchains that only provide data availability and consensus, and leave execution to specialised rollups, are designed to provide secure, scalable, and interconnected application ecosystems.
StarkNet zk-STARK Powered Performance
To enhance throughput and cost reduction, StarkNet relies on zk-STARK proofs, which are a form of cryptography that does not need a trusted setup, unlike other cryptographic methods. It has a modular structure that isolates computation, settlement and data availability to give optimum performance.
Use Cases in the Real World That Matter in 2026
Modular blockchains and ZK proofs would be mere concepts to talk about without their practical use in different industries. This is the place where the value is currently manifesting itself:
High-Throughput Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
DeFi has never been able to expand due to scalability. ZK rollups address that by improving the efficiency with which to handle transaction proofs, compressing them and settling on main chains, reducing gas costs and enabling DeFi to be used by ordinary people.23 Institutions currently trying real-time settlement and liquidity markets on these networks.
Enterprise and Regulatory Compliance
Zero-knowledge proofs enable businesses to prove adherence to requirements without revealing confidential information. This opens the use of blockchain to such sectors as banking, supply chain and healthcare, where privacy cannot be compromised, yet verification is vital. The fact that it is possible to demonstrate the correctness without providing trade secrets or patient information is a breakthrough in terms of the adoption of blockchain in an enterprise.
Gaming & Digital Economies
Gaming ecosystems require high throughput and low costs that allow masses of players and micro-transactions. Such projects as Lumina ZK Rollup construct modular worlds that present tens of thousands of transactions per second, driving new play-to-earn and asset-ownership frameworks at scale.
Identity & Privacy Systems
Zero-knowledge proofs are used to power systems in which users are able to demonstrate properties (such as age or citizenship) without revealing their identity. This is essential to the Web3 identity systems, and it can re-establish trust online without violating privacy.
Data Checking & Computation Checking
Space and Time offer ZK-verified queries to on-chain and off-chain data to allow enterprises to use blockchain-verified analytics in current data infrastructures.
The Roadmap of Ethereum: The Big Picture Shift
Ethernet, the leader of smart contracts blockchain, has successfully established the blueprint of the future blockchain infrastructure.
By the beginning of 2026, Vitalik Buterin and colleagues described a roadmap where PeerDAS (data availability sampling) will be operational on mainnet and ZK-EVMs will be at the production level. This is to say that Ethereum is deploying the same technologies that can deliver the simultaneous security, decentralisation and scalability – in effect addressing the so-called blockchain trilemma with actual running code.
The rollouts of Ethereum are organised in the following way:
- 2026: Gas limit increments through Bandwidth Allocation Limits (BALs) and proposeter-builder separation (ePBS) enshrined. Initially, the opportunities to participate in ZK-EVM nodes are created.
- 2026-2028: Structural changes of the state and repricing that readies the network to even greater throughput.
- 2027-2030: ZK-EVMs are made the default block validation mode, which will again increase bandwidth and cost-reductions without compromising on decentralisation.
This is a level of improvement, but not the level of incremental improvement, but rather an architectural change that makes scalability a protocol-level feature.

Ethereum is leading blockchain’s future with PeerDAS and ZK-EVMs, tackling security, decentralisation, and scalability at the protocol level. (Image Source: BitcoinBlog.de)
Reasons Why Analysts Think 2026 Will Be a Breakout Year
The pundits of the blockchain industry now claim that 2026 will be remembered as a period in which scaling technology was achieved. The reasoning is simple:
- Validation does not require re-executing all the transactions to ensure that they are correct. They can just check compact ZK proofs – reducing overhead by a factor of many orders of magnitude and allowing even modest hardware such as smartphones to be involved in validation with no specialised hardware.
- Layers of modular data availability, such as Celestia, distribute the heavy load of storage to eliminate bottlenecks that had slowed blockchains in the past as they scaled.
Scalable, secure, customisable and practical, this is the technology which experts refer to as blockchain infrastructure 2.0.
Also Read: Trump Crypto Influence: How 2025 Shaped the Cryptocurrency Market 2026
Institutional and Regulatory Themes
Another large aspect of the next chapter of blockchain is on real-world regulation and adoption:
Institutional Adoption
Both ZK rollup systems and modular frameworks are piloted by large banks and other financial institutions since they are efficient and ensure compliance with the law. There is an estimation that the ZK market may be valued in billions of dollars when scalability and privacy can be made commercial.
Government and Central Bank Applications
The central banks looking into the digital currencies (CBDCs) prefer hybrid structures in which the governance and privacy can be balanced. Zero-knowledge proofs allow regulators to ensure properties even without revealing transaction data privately – a formidable tool in sovereign digital finance.
Blockchain Implementation in the Enterprise
The modular design is being tried in blockchain consortia in supply chains, identity, and health records because it gives them control over the data availability and execution environments separately – essential in regulatory compliance and auditable workflows in high-risk industries.

ZK and modular blockchains power scalable, private, and compliant finance and enterprise solutions. (Image Source: LinkedIn)
Reflections and Conclusions: The 2026 Blockchain Inflexion Point
By early 2026, the blockchain industry will no longer be talking about the potential of scale, but will actually be rolling it out. ZK technology and modular architectures are not what is to be later on; they are contemporary, and undergoing development and implementation. This transformation changes the possibilities of Web3.
Today, the applications unlocking value are based on this new orchestration of the infrastructure, whether in DeFi and gaming or enterprise and compliance. The next chapter of blockchain is not about speculation but one of engineering breakthroughs, which makes the use of blockchain utility-scale possible.
When you are addressing a group of professionals and novices simultaneously, this is the ideal moment, when code meets capability, to make the narrative shift. The technology has ceased to be theoretical. It is lively and creating the future of decentralised systems right before our eyes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What do the actual advances on ZK-EVMs look like by early 2026?
Ans: Ethereum developers state that ZK-EVMs have already reached production-quality performance in alpha environments. Components of Ethereum are already using them this year in a transitional phase. - Are modular blockchains live today?
Ans: Yes. Modular data layers such as Celestia and execution systems such as zkSync Hyperchains are operational and helping developers build customised blockchain applications. - Is the blockchain trilemma really resolved?
Ans: According to the latest announcements, the combination of data availability sampling and zero-knowledge validation is practically solving the balance of decentralisation, security, and scalability on major networks. - When will Ethereum fully transition to ZK-based validation?
Ans: As per Vitalik Buterin’s roadmap, ZK validation is expected to become the standard approach between 2027 and 2030, as part of a gradual transition that ensures safety and network stability. - What are the effects of these technologies on everyday users?
Ans: Users can expect reduced fees, faster transactions, and enhanced privacy. Developers gain tools to create complex, scalable applications, and validators can participate with less specialised hardware. - What is zero-knowledge technology on a blockchain?
Ans: ZK technology allows one party to prove to another that a statement is true without revealing the underlying information. It enables private verification of transactions or computations and is fundamental to scaling rollups and privacy protocols. - Why are modular blockchains significant?
Ans: Modular blockchains separate execution, consensus, and data availability layers. This improves scalability and flexibility, allowing developers to create customised blockchain environments optimised for specific tasks.

