Meta is no longer playing around with the fringes of artificial intelligence. It is heading right to the heart.
The purchase of Manus AI by the company signifies an important turn in the way the new AI system will operate, act, and treat the world. It is not that chatbots can respond to questions. It concerns free agents who strategize, make decisions and take actions with the least amount of human intervention.
Meta puts itself at the heart of the race to really self-directed artificial intelligence in a single move. And the timing matters.
In the tech sector, there is moving on the focus of large language models that simply respond to systems that work. Manus AI is right in that bracket.

Meta’s Manus AI deal marks a shift from chatbots to autonomous, self-directed AI. (Image Section: The Register)
The Essential Facts, Up Front
Meta has acquired Manus AI, which is a rapidly growing company devoted to autonomous AI agents capable of performing complex and multi-step tasks without constant encouragement.
Manus agents do not pause and wait to be instructed at each point, unlike traditional AI tools. They examine goals, divide them into tasks, adapt to challenges, and accomplish tasks on their own.
In the case of Meta, this purchase enhances its effort to leave their generative AI behind and move to agentic systems that have the potential to drive platforms, businesses, and daily workflows.
To the industry, it is a clear signal that autonomous agents are not experimental anymore. They are gradually turning into pillars.
The Difference With Manus AI
Manus AI does not present itself as a different conversational model. Its strength is based on execution. Manus agents are less of assistants than digital workers. They can:
- Set goals
- Plan workflows
- Use tools and data sources
- Monitor progress
- Make real-time adjustments
The design will enable Manus agents to operate on longer time horizons. They don’t just answer. They perform, analyze results, and proceed. It is this ability that technological powerhouses are now competing to develop.
Why Meta Moves Now
The move by Meta to purchase Manus AI is part of a larger industry trend that already exists.
Big language models have come of age. Their limitations are clear. They are really brilliant in their responses, but what they need is people to make the process go. Self-directed agents eliminate such a bottleneck.
In the case of Meta, the strategic appeal is self-evident. The firm has some of the biggest platforms in the world, including social networks and business applications. Every platform creates a lot of work, mod-work, content movements, ad-optimisation issues and customer relationships.
Self-agents will undertake those tasks and continue to do so at scale and with more and more autonomy. Meta is not simply purchasing technology. It is buying leverage.
The Rise of Agentic AI
The most crucial frontier of AI for the industry is agentic AI. The agentic systems are not characterized by a one-time prompt-response loop, but rather by processes. They reason, act, and adapt.
This transformation transforms the role of AI in everyday life. Instead of opening an application and giving orders, users specify results. The agent handles the rest.
This is why independent agents have taken a leading role in discussions in AI laboratories, venture capital, and company strategies. Manus AI fits quite well in this transition.
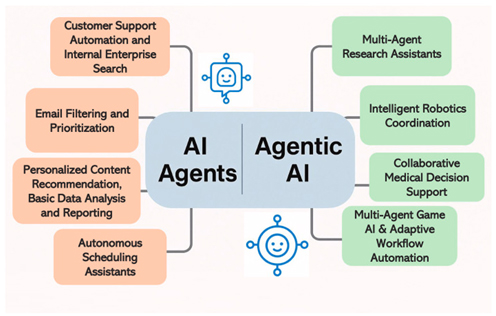
Agentic AI lets systems act, reason, and adapt on their own, placing Manus AI at the forefront of this shift. (Image Source: ScienceDirect.com)
From Assistance to Autonomy
The distinction between help and independence is not as obvious as it might seem to be. Humans are assisted by AI to work more rapidly. The whole step of the working process is substituted with autonomous AI.
The consequences of that leap are economic, social and technological. In business, independent agents lessen the friction in business. They can be used to automate logic in development. They control production cycles in content systems.
The acquisition has placed Meta in the position of integrating autonomy within the consumer and enterprise tools. This is not a future roadmap. It is a present-day pivot.
Why This Matters Beyond Meta
There is no vacuum in this deal. Competition is increasing across the AI. Technological giants are not competing anymore to create the smartest model. They are competing to develop the most competent system.
They are autonomous agents that are at the core of that competition. Anyone who owns agent infrastructure determines the subsequent digital labour wave. The decision that Meta takes demands that competitors pick up their pace or risk being left behind in their agent programs.
The Connection to General Intelligence
Self-directed agents are commonly considered to be on the way to artificial general intelligence. Not because they reason as humans, but because they act as systems whose purpose is to achieve.
Even general intelligence needs more than language. It involves planning, persistence and environmental adaptation. The architecture of Manus AI is in close correspondence with such requirements.
An acquisition of Manus provides Meta with a platform with the ability to develop wider intelligence, as opposed to being restricted to specific tasks. This is important since the direction of general intelligence is progressively controlled by agent design rather than by model size.
The Application in Practice Coming to Life
The attractiveness of Manus AI lies in the fact that its agents can be readily transformed into practice.
- Agents control the reporting cycles and internal workflow in business operations.
- Agents track campaigns and make changes and examine variations in digital marketing.
- Agents in research settings collect data and execute analysis loops and summarise findings unsupervised.
The capabilities scale quickly in the case of the ecosystem of Meta. Agents do not get tired. They do not queue tasks. They are twenty-four-hour shifts.
The Shift of Emotions: Leaving Machines to It
Psychological is one of the least thought-about parts of autonomous AI. Human beings feel free to pose questions to AI. They feel less satisfied with allowing AI to be free.
The acquisition of Meta brings that discussion to the light. Users will have to deal with a new reality as autonomous agents enter mainstream platforms. AI will not give suggestions, but decisions.
The change of such a shift needs trust, openness, and guardrails. The design of Manus AI focuses on controllable autonomy, where humans can set boundaries without having to micromanage the execution process. They are vital because they increase the ability of agents.
The Future of the AI Arms Race Gets a New Phase
This acquisition is an indication of further escalation. The AI arms race does not concern the size of the model trained anymore. It is concerning who has the most efficient agents.
Self-directed systems alter the battle of wits. They accrue productivity increases. They reduce human overhead. They scale decision-making.
The shift that Meta makes speeds up such a race. All the big players have been given the option to either develop agents, buy them or be aggressive in forming partnerships. It is no longer possible to stay put.

Meta’s move sparks a new AI race focused on efficient, self-directed agents. (Image Source: VentureBeat)
Going Forward: The Second Book of Innovation
The acquisition of Manus by Meta is not merely a milestone but the point in the development of autonomous software that thinks and acts. In 2026 and beyond, we may see:
- A greater connection of the agents to daily productivity tools in industries.
- Specialised agents marketplaces where plug-and-play systems are appropriate to education, healthcare, finance and logistics, among others.
- Hybrid human-agent teams, in which decisions are collectively co-created.
- New safety and governance standards that are coming out from boththe industry and governments.
It is not going to be about what AI will answer, but what AI will do on behalf of human beings. This is the border of freedom – and this is exactly where Meta finds itself after buying it – right at the heart of that developing narrative.
Also Read: How AI Forecasting Tools are Transforming Emergency Healthcare: Reducing A&E Waiting Times in 2025
Conclusions: A New Age of Thinking Action
The acquisition of Manus AI by Meta is not simply a new technology stack for the latter. It hastens the transformation of stagnant tools into moving partners.
This is a breathtaking moment to innovators, creators, business leaders and curious users alike, where intelligence is not merely calculated but made actionable on behalf of human intent. The world is watching. The race is on. And independent agents have now been made centre stage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the biggest reputation of Manus AI?
Ans: Manus AI focuses on autonomous agents, which are capable of planning and executing complex tasks with little human supervision. - What is the significance of autonomous AI agents?
Ans: They bring AI out of response-based tools and into systems capable of running across workflows on their own. - What impact does this have on the average user?
Ans: In the long term, there will be a reduction in user engagement with prompts and an increase in user outcomes as the agents undertake jobs in the background. - Does it take AI towards general intelligence?
Ans: The use of autonomous agents brings about goal-driven behaviour for researchers, which many see as a key step towards broader intelligence. - Will the autonomous agents take over jobs?
Ans: They are more likely to take over operations rather than jobs, particularly tasks that are laborious or procedure-intensive. - Why are Manus agents better than previous AI tools?
Ans: Manus agents are designed to plan and implement actions independently, without necessarily relying on prompts—unlike traditional AI tools. - Will Manus keep its brand and users after being acquired?
Ans: Meta has committed to keeping Manus as a standalone product while also integrating its technology into extended offerings. - Does this deal make a difference financially?
Ans: The acquisition is reportedly between 2 and 3 billion dollars, making it one of Meta’s largest AI acquisitions to date. - What will this mean for data security and privacy?
Ans: Meta has emphasised that Manus can reduce Chinese links to operations and strengthen data security, signalling a focus on safer deployment. - Is the use of autonomous agents safe in business?
Ans: Governance is required to ensure safety. Companies should implement strong policies to trace, verify, and certify agent activities, aligning them with business objectives and ethical standards.

